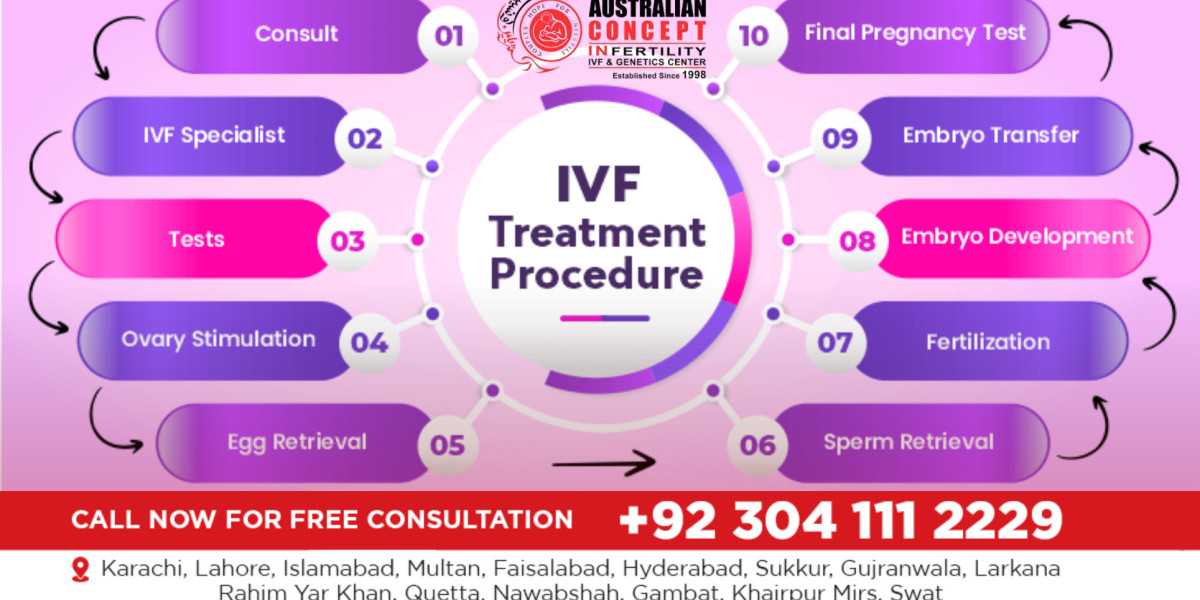
In vitro fertilization (IVF) is one of the most well-known and effective treatments for infertility. Whether you're dealing with male infertility, female infertility, or unexplained reproductive issues, IVF offers hope. This article will guide you through the IVF process, explaining each step with clarity and detail to help you understand the journey ahead.
1. Initial Consultation and Pre-Treatment Evaluation
The first step of the IVF process is an initial consultation with a fertility specialist. During this visit, the doctor will gather your medical history, review any previous fertility treatments, and assess the underlying cause of infertility. Both partners may undergo a series of tests, including:
Blood tests: To check hormone levels and screen for underlying conditions.
Ultrasound exams: To evaluate the condition of the ovaries and uterus.
Semen analysis: For the male partner, to assess sperm count, motility, and morphology.
The fertility doctor will use this information to personalize your IVF plan and suggest the best course of action.
2. Ovarian Stimulation (Egg Retrieval Preparation)
The next step is to stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs. In a typical menstrual cycle, only one egg is released, but IVF requires several eggs for better chances of fertilization.
Medications: The woman will start taking fertility medications (usually injectable hormones such as FSH and LH) for 10-14 days. These hormones stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs, rather than just one.
Monitoring: During this period, you’ll visit the clinic for regular blood tests and ultrasounds to monitor hormone levels and track the growth of the follicles (fluid-filled sacs in the ovaries where eggs mature). This allows the doctor to adjust medication dosages as needed.
Trigger shot: Once the eggs are mature, a final injection of hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) is given to trigger ovulation, preparing the eggs for retrieval.
3. Egg Retrieval (Aspiration)
Once the eggs are ready, the next step is egg retrieval, also known as aspiration. This procedure is typically done under light sedation, so you won’t feel pain. The fertility doctor uses an ultrasound-guided needle to retrieve the eggs from the ovaries.
The procedure typically takes about 20-30 minutes.
The eggs are collected and taken to the laboratory for fertilization.
4. Sperm Collection and Preparation
On the same day as the egg retrieval, the male partner (or sperm donor) will need to provide a sperm sample. The sperm is then processed in the laboratory to select the healthiest sperm for fertilization.
Sperm washing: The sperm is cleaned and concentrated to remove any impurities, and the best-quality sperm is selected for fertilization.
In some cases, if male infertility is an issue, a procedure called intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) may be used. In ICSI, a single sperm is directly injected into an egg, increasing the chances of successful fertilization.
5. Fertilization
The next step is fertilization, where the eggs and sperm are combined in the laboratory. There are two main approaches to this:
Conventional IVF: Eggs and sperm are mixed together and left to fertilize naturally.
ICSI: In cases of male infertility or when conventional IVF is less likely to succeed, ICSI is used to directly inject a sperm into each egg.
The fertilized eggs are monitored for growth and development over the next few days.
6. Embryo Culture and Monitoring
After fertilization, the embryos are cultured for several days. They are closely monitored in the lab to check for healthy division and growth. On day 3 or 5, the embryos are assessed for quality. The embryologist will decide how many embryos are suitable for transfer.
Day 3 embryos: These are early-stage embryos with a smaller number of cells.
Day 5 (blastocyst stage) embryos: These are more developed embryos and are often the preferred choice for transfer due to higher success rates.
In some cases, genetic screening may be done at this stage, especially for patients at risk of passing on genetic disorders. This is known as preimplantation genetic testing (PGT).
7. Embryo Transfer
Embryo transfer is a relatively simple and non-invasive procedure. The most viable embryos (usually 1-2) are selected and transferred into the woman's uterus using a thin catheter. No anesthesia is required, and the process typically takes only 10-15 minutes.
The number of embryos transferred is determined based on the woman's age, embryo quality, and overall health.
The doctor may recommend transferring more than one embryo in cases of advanced maternal age or previous IVF failures.
After the embryo transfer, the woman may be given hormone supplements (like progesterone) to support the uterine lining and help the embryo implant successfully.
8. Pregnancy Test and Follow-Up
About 10-14 days after the embryo transfer, the woman will undergo a blood test (beta hCG) to determine if implantation has occurred and if she is pregnant. If the test is positive, further monitoring with ultrasounds and blood tests will be done to confirm the pregnancy and check the development of the embryo.
If the test is negative, the fertility clinic will guide you through the next steps, which may include considering a subsequent IVF cycle or exploring other fertility options.
9. Early Pregnancy and Ultrasound Monitoring
If the pregnancy test is positive, an ultrasound will be performed to check for a heartbeat and the viability of the pregnancy. The doctor will continue to monitor the pregnancy in its early stages and offer support as necessary.
10. Freezing Extra Embryos (Optional)
In cases where extra healthy embryos remain after the transfer, they may be frozen for future use. This is known as embryo cryopreservation. These frozen embryos can be thawed and transferred in a subsequent IVF cycle if needed.
Conclusion
IVF is a complex but highly effective process that offers hope to many couples facing infertility. Understanding the step-by-step process can help reduce anxiety and make the journey more manageable. While IVF success rates vary depending on individual circumstances, it remains one of the most successful assisted reproductive technologies available today.
For More Details: https://australianconcept.com/ivf/